Workers in a wide variety of industries are exposed to potential hazards on a daily basis. It’s up to employers to provide them with the personal protective equipment (PPE) required to mitigate those hazards. This article will offer an introduction to the basic types of PPE and when they should be used to help employers understand their options.
- Eye and Face Protection
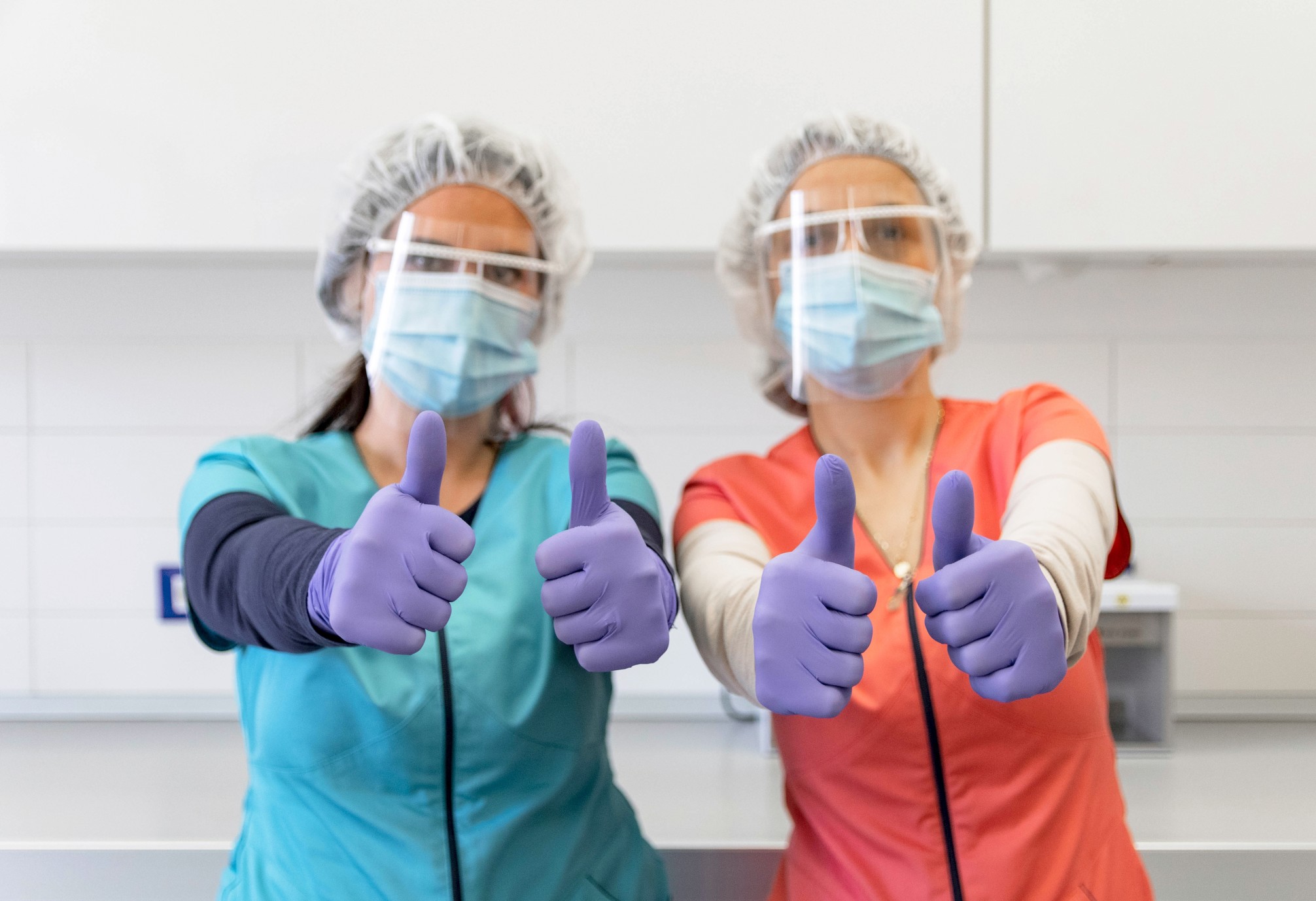
PPE that provides eye protection usually comes in the form of specialized goggles or glasses. Some types of eye protection are designed to prevent chemical splash exposure, while others protect workers who use lasers or may be subjected to impacts from flying debris. Face shields are also available to protect workers from chemical splashes or biological hazards and are usually worn in conjunction with specialized respiratory protective equipment and splash goggles.
- Hand Protection
This category of PPE refers to specialized gloves. It’s important to keep in mind that gloves used as PPE are designed with very specific purposes in mind, and no pair of gloves will be impervious to all potential hazards. Employers need to evaluate the types of hazards their workers may be exposed to before purchasing gloves.
In some cases, disposable latex, nitrile, or vinyl gloves may be enough to protect workers. They’re usually used when working with biological hazards. Insulated gloves are used to protect against heat and extreme cold.
Chemical resistant gloves are used when working with corrosive liquids, flammable compounds, and organic solvents. They come in multiple thicknesses to accommodate all kinds of work and potential exposure issues.
- Body Protection
Full body protection also comes in many forms. Traditional body protection is only appropriate for reducing exposure risks from dirt, inks, and non-hazardous biological or chemical agents. For more dangerous applications, full barrier protection is more appropriate for working with infectious materials, while flame-resistant clothing should be worn while working with air- or water-reactive chemicals and organic solvents.
- Respiratory Protection
With the exception of basic surgical masks, respiratory protective PPE needs to be properly fitted to the wearer’s face in order to be effective. N-95 respirators, half-mask respirators, and full-face respirators all need to be fit-tested. All of these options are appropriate for working with live animals and infections materials, but only half-mask and full-face respirators are appropriate for combating chemical vapours.
- Hearing Protection
Hearing protection should be made available to anyone who works in an environment with high noise exposure. Affected employees may include not just construction workers and machinists, but also laboratory workers, factory workers, and many others. Disposable earplugs, reusable earplugs, and hearing bands are all viable options for working in areas where sound levels rise above an average of 85 decibels.
Where to Buy PPE
Now that employers have an idea of what types of PPE, they may need to provide to their workers to keep them safe and healthy, it’s time for them to start looking into vendors. Make sure the vendor complies with OSHA and ANSI standards and offers fast product delivery to accommodate rush orders. Visit https://www.premiersafety.com/shop-by-category/personal-protective-equipment-ppe/to browse through personal protective equipment and other essential safety products and place an order today.